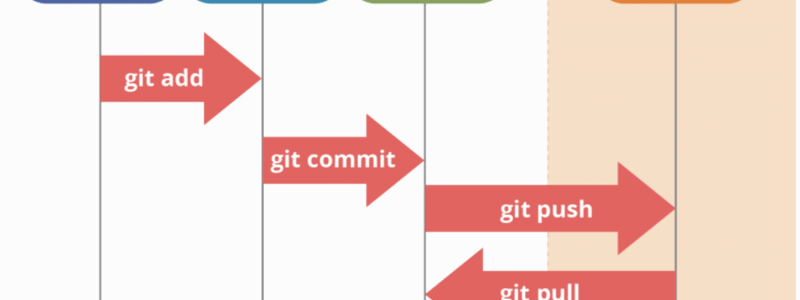
Streamlining Git Workflows for Developers and Operators
Managing code in a collaborative environment can be challenging, especially when multiple team members contribute to the same project. In this post, we’ll explore three common Git workflows that programmers and operators use daily:
- Adding a feature (multi-day development).
- Pulling the “latest dev” to a test environment.
- Pulling the “latest main” to a production environment.
Let’s dive into the practical steps for each workflow.
1. Adding a Feature
Developing a new feature often spans several days and involves regular updates to keep up with the development branch (dev). Here’s a step-by-step guide for programmers:
Steps:
- Create a feature branch:
- Start by switching to the
devbranch and ensuring it’s up-to-date. Then, create a new branch for your feature: git checkout devgit pull origin devgit checkout -b feature/<feature-name> dev
- Start by switching to the
- Work on the feature:
- As you develop, make incremental changes and commit regularly
git add <files>git commit -m "Descriptive commit message"
- Stay updated with
dev:- Periodically pull the latest changes from
devto avoid conflicts: git fetch origingit rebase origin/dev
- Periodically pull the latest changes from
- Merge the feature branch back into
dev:- When the feature is complete, merge it into
dev: git checkout devgit pull origin devgit merge feature/<feature-name>git push origin dev
- When the feature is complete, merge it into
- Clean up the feature branch:
- After merging, delete the feature branch both locally and remotely:
git branch -d feature/<feature-name>git push origin --delete feature/<feature-name>
2. Pulling the Latest dev to a Test Environment
For operators managing deployments to test environments, staying synchronized with the dev branch is essential. Here’s how to do it:
Steps:
- Switch to the
devbranch:- Ensure you’re on the correct branch:
git checkout dev
- Pull the latest changes:
- Fetch and apply the newest updates from the remote repository:
git pull origin dev
- Deploy to the test environment:
- Use your deployment tools or scripts to update the test environment with the latest code.
3. Pulling the Latest main to a Production Environment
Deploying to production requires working with the stable main branch. Here’s how operators can pull and deploy the latest production-ready code:
Steps:
- Switch to the
mainbranch:- Always verify that you’re working on the
mainbranch before proceeding: git checkout main
- Always verify that you’re working on the
- Pull the latest changes:
- Update your local branch with the latest production code from the remote repository:
git pull origin main
- Deploy to production:
- Use your production deployment process to apply the updated code.
Best Practices
To ensure smooth collaboration and minimize conflicts, follow these tips:
- Work in branches: Always create feature branches for development tasks.
- Keep branches updated: Regularly pull changes from
devormainto stay in sync with the team. - Clean up old branches: Delete branches after they’ve been merged to keep the repository tidy.
- Test thoroughly: Always test in the test environment before deploying to production.
- Use descriptive commit messages: Make it clear what each commit accomplishes.
By adhering to these workflows, your team can streamline development and deployment processes while maintaining a clean, organized repository.